NEW ALTERNATIVE
The Duodenal Switch (DS), also known as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS), is a type of bariatric surgery designed for significant weight loss. It is a more complex procedure that combines aspects of both restrictive (reducing stomach size) and malabsorptive (limiting nutrient absorption) methods. The surgery involves removing a portion of the stomach and rerouting a significant part of the small intestine, which changes how the digestive system processes food and absorbs nutrients.
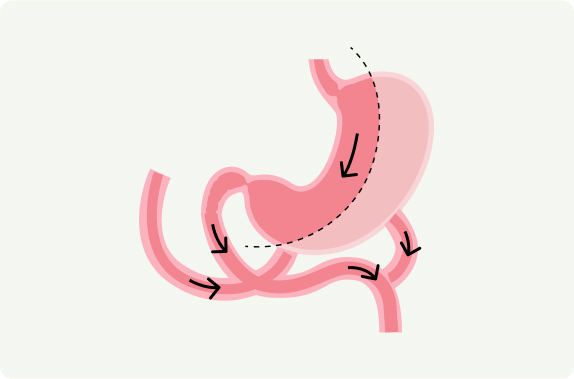
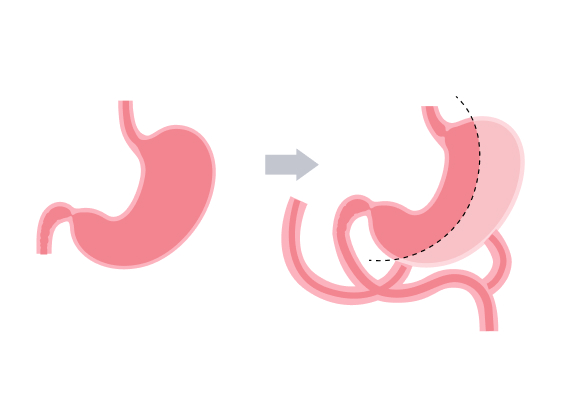
Procedure Overview:

Significant Long-Term Weight Loss: DS leads to the highest average weight loss of any bariatric procedure. Patients can expect to lose 70-90% of their excess body weight within 2 years.
Improvement or Resolution of Obesity-Related Conditions: Type 2 Diabetes: DS has the highest success rate for remission of type 2 diabetes compared to other bariatric surgeries. Hypertension and hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol) are often significantly improved or resolved. Obstructive sleep apnea and joint pain related to obesity typically improve.
Metabolic Benefits: Beyond weight loss, the duodenal switch is known for its powerful metabolic effects, which can help improve insulin sensitivity and other markers of metabolic health.
Lower Risk of Weight Regain: Due to the malabsorptive component of the surgery, long-term weight regain is less common than in other surgeries, such as the sleeve gastrectomy or gastric banding.
Increased Eating Capacity: Compared to other restrictive surgeries like the gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, patients have a slightly larger stomach, allowing them to eat more variety in foods (but still in smaller portions than before surgery).
Considerations:
Community Questions
How does the duodenal switch differ from other weight-loss surgeries?
The duodenal switch combines two approaches: a restrictive component (removing a portion of the stomach to limit food intake) and a malabsorptive component (rerouting the small intestine to limit nutrient and calorie absorption). This combination makes it one of the most effective surgeries for long-term weight loss and improvement in metabolic conditions. Unlike other surgeries, it has a more profound effect on fat and nutrient absorption.
What are the risks and complications associated with duodenal switch surgery?
The duodenal switch is a complex procedure with higher risks compared to other weight-loss surgeries. Potential complications include:
How much weight can I expect to lose with the duodenal switch?
On average, patients lose about 70-90% of their excess body weight within two years after surgery. This procedure offers the highest average weight loss of all bariatric surgeries. Weight loss success depends on the patient’s adherence to dietary guidelines, exercise, and follow-up care.
Will I need to take vitamins or supplements after duodenal switch surgery?
Yes, lifelong supplementation is critical due to the malabsorption aspect of the surgery. Commonly required supplements include multivitamins, calcium, vitamin D, vitamin A, vitamin E, vitamin K, iron, and protein supplements. Regular blood work is necessary to monitor nutrient levels and adjust supplementation as needed.
What kind of lifestyle changes are required after duodenal switch surgery?
Patients must make significant lifestyle changes, including:
Ready to Schedule a Consultation?
Transformations Happen Daily at Grand Health Partners! Take the first step to life change and schedule a consultation with our office.